浅析java线程中断机制
分析java线程中断的作用、使用场景以及处理原则
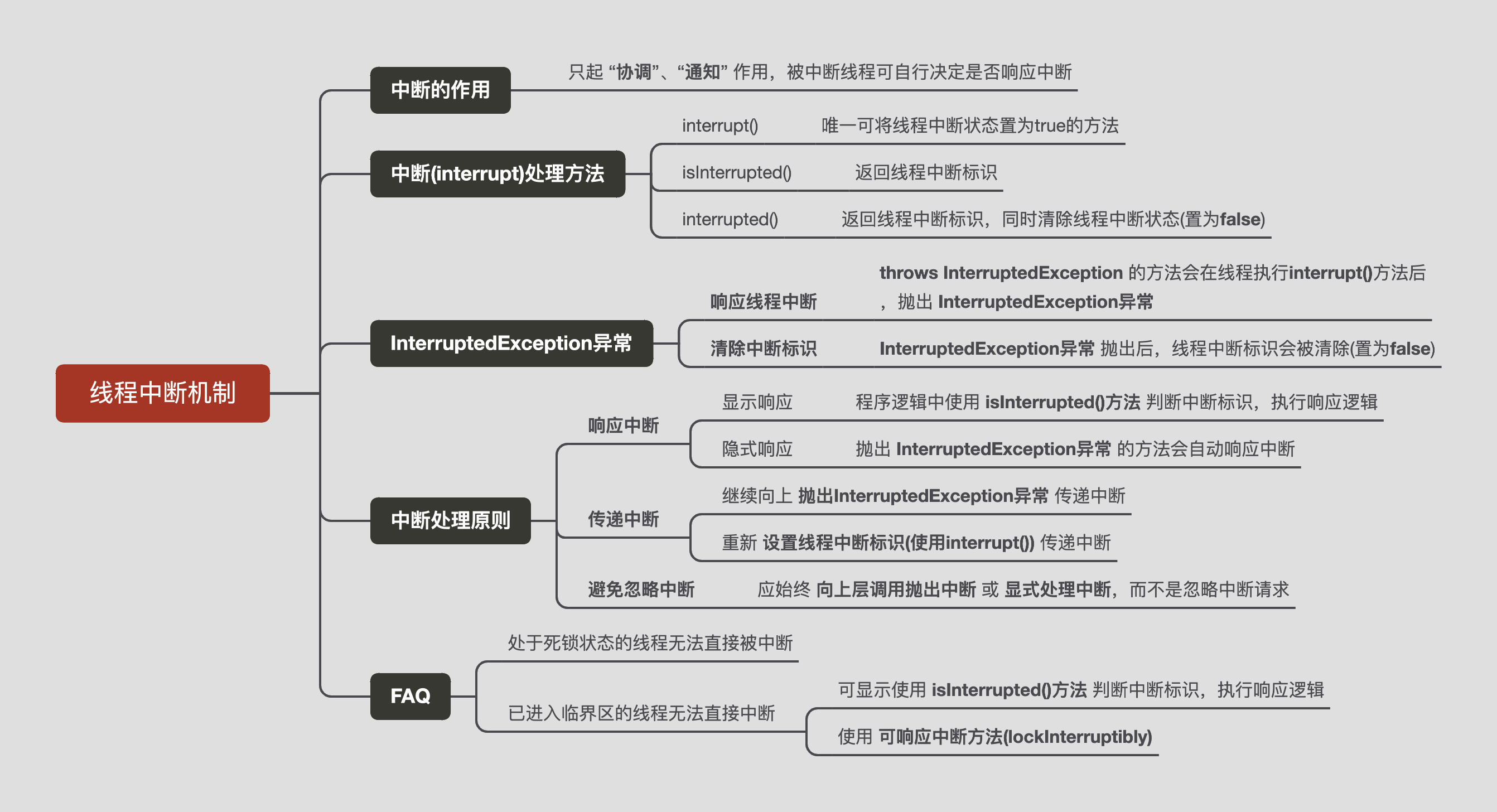
线程中断机制-知识图谱
线程中断处理方法
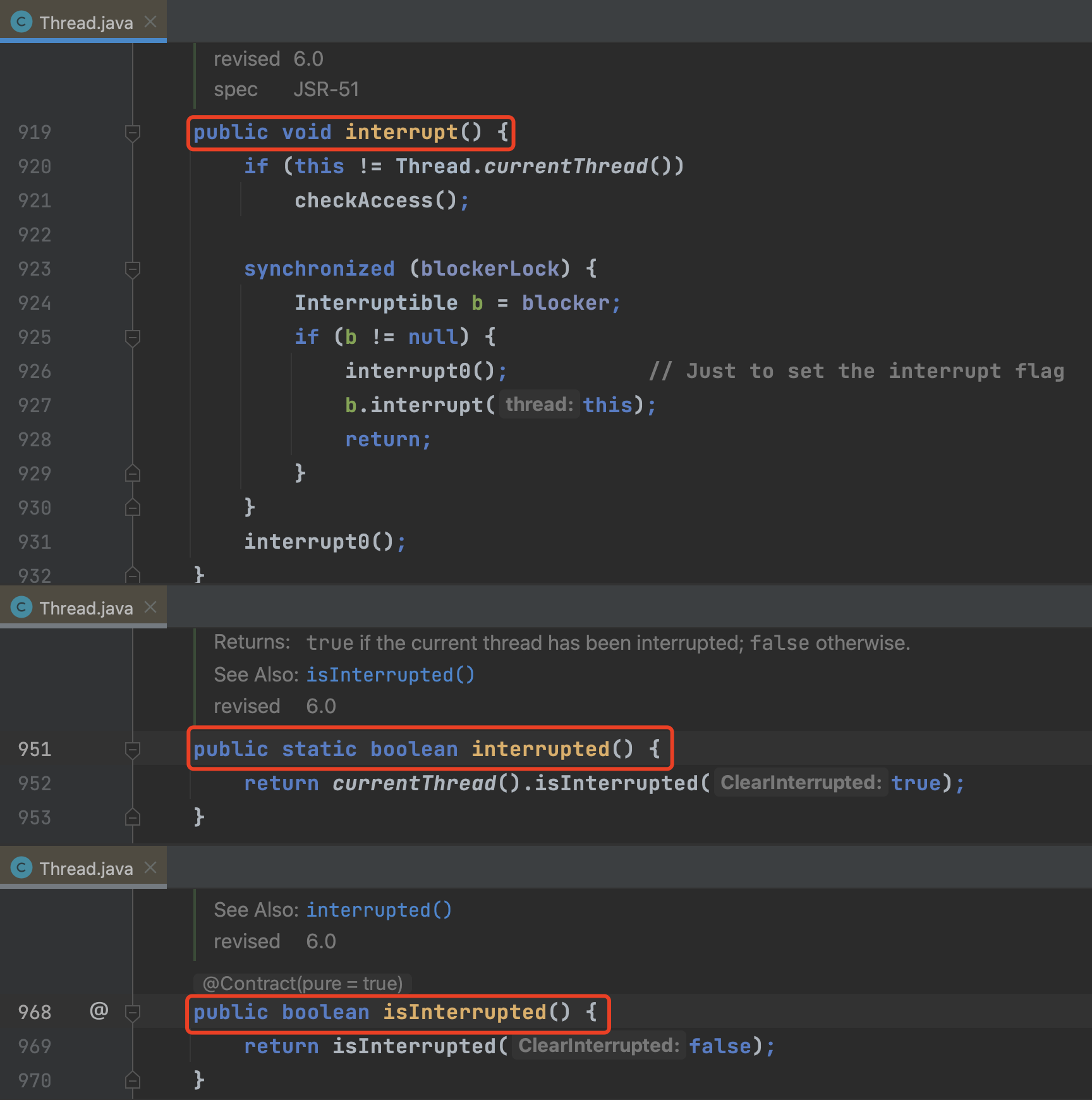
Thread类中有3个与线程中断有关的方法:
interrupt(): 唯一一个可将线程 中断标识 置为 true 的方法isInterrupted(): 返回线程 中断标识。interrupted(): 返回线程 中断标识,并 清除 线程中断标识(即若当前线程被中断,且中断标识为 true,则调用interrupted()方法后,会返回 true,同时将线程中断标识置为 false)。
中断(Interrupt)作用
Java语言中的 中断(Interrupt) 与中文语境中中断的含义略有不同;在Java语言中,线程 中断(Interrupt) 并不是真正的将某个运行中的线程终止,中断(Interrupt)的作用 更接近于 协调 和 通知;至于收到中断信号的线程如何响应(终止、继续执行 或 挂起等),由被中断线程自己决定。
程序示例
public class SleepTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread c = Thread.currentThread();
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 此处sleep()只起阻塞作用, 也可替换成空转的for消除try..catch语句
Thread.sleep(2000L);
c.interrupt();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
t.start();
System.out.println("------ thread start! ------");
// 实践证明:interrupt()方法只会将线程的中断标识置为true, 无法终止线程运行,只起协同(通知)作用,具体执行怎样的逻辑,取决于代码对中断的响应
try {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("exception occurs!");
// 注: 抛出InterruptedException异常后,中断标识会被置为false
System.out.println("interrupt status - " + c.isInterrupted());
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("线程状态: " + Thread.currentThread().getState());
}
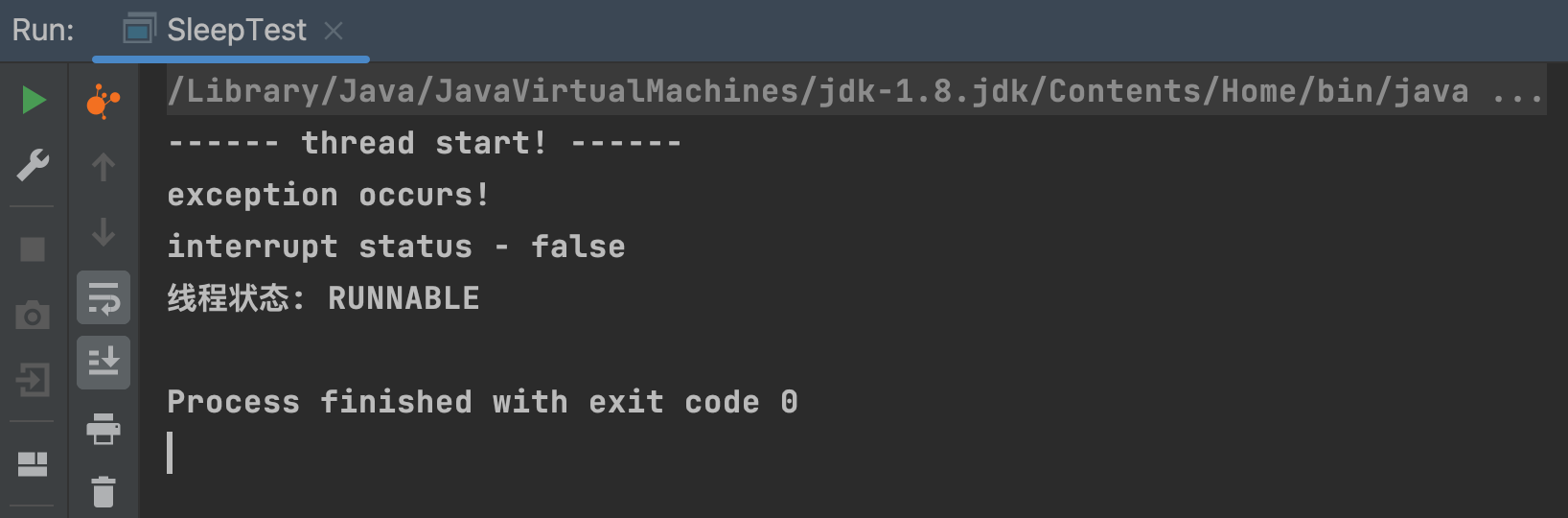
可以看到 Thread.sleep() 方法会可以感知中断,并抛出InterruptedException异常,
其他会抛出 InterruptedException异常 的方法包括但不限于:
wait()sleep()join()offer()take()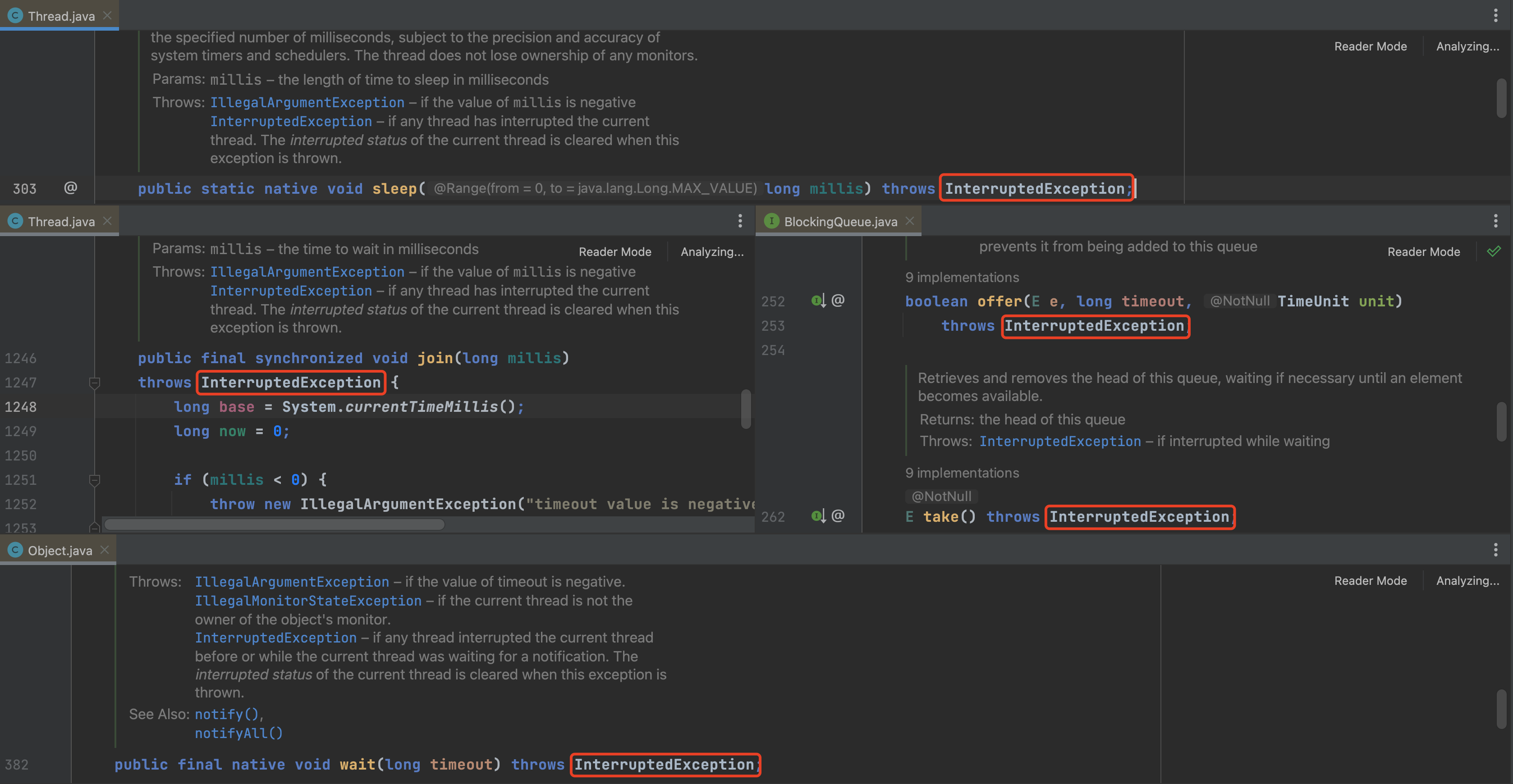
需要特别说明,抛出 InterruptedException异常 后,中断标识会被清除(重置为 false)。
中断处理原则
- 响应中断
- 显示响应
程序逻辑中使用 isInterrupted()、interrupted() 方法判断中断标识,执行响应逻辑。 - 隐式响应
方法声明中包含 throws InterruptedException 的方法会自动响应中断。
- 显示响应
- 传递中断
当其他线程调用另一个线程的 interrupt() 方法中断它时,应该将中断传递给被中断线程。
处理方法:- 继续向⽅法调⽤栈的上层抛出 InterruptedException异常 传递中断
- 重新设置线程中断标识(使用interrupt()) 传递中断
- 避免忽略中断
程序中捕获的InterruptedException中断异常, 不应被吞掉。
程序示例public class SleepTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread c = Thread.currentThread(); Thread t = new Thread(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(2000L); c.interrupt(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }); t.start(); System.out.println("------ thread start! ------"); // 测试 printStackTrace()方法 是否会吞掉异常 while(true) { System.out.println("running!!!"); if (c.isInterrupted()) { break; } try { // 当线程被阻塞在 sleep()/join()/wait() 这些方法时, 如果被中断, 就会抛出 InterruptedException 受检异常, // 并且,当前线程的中断标识会被清除(置为false) Thread.sleep(1000L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // printStackTrace()会吞掉异常 e.printStackTrace(); // 方法1: 重置中断标识 // c.interrupt(); // 方法2: 向⽅法调⽤栈的上层抛出受检异常 // throw new RuntimeException(e); } } } }
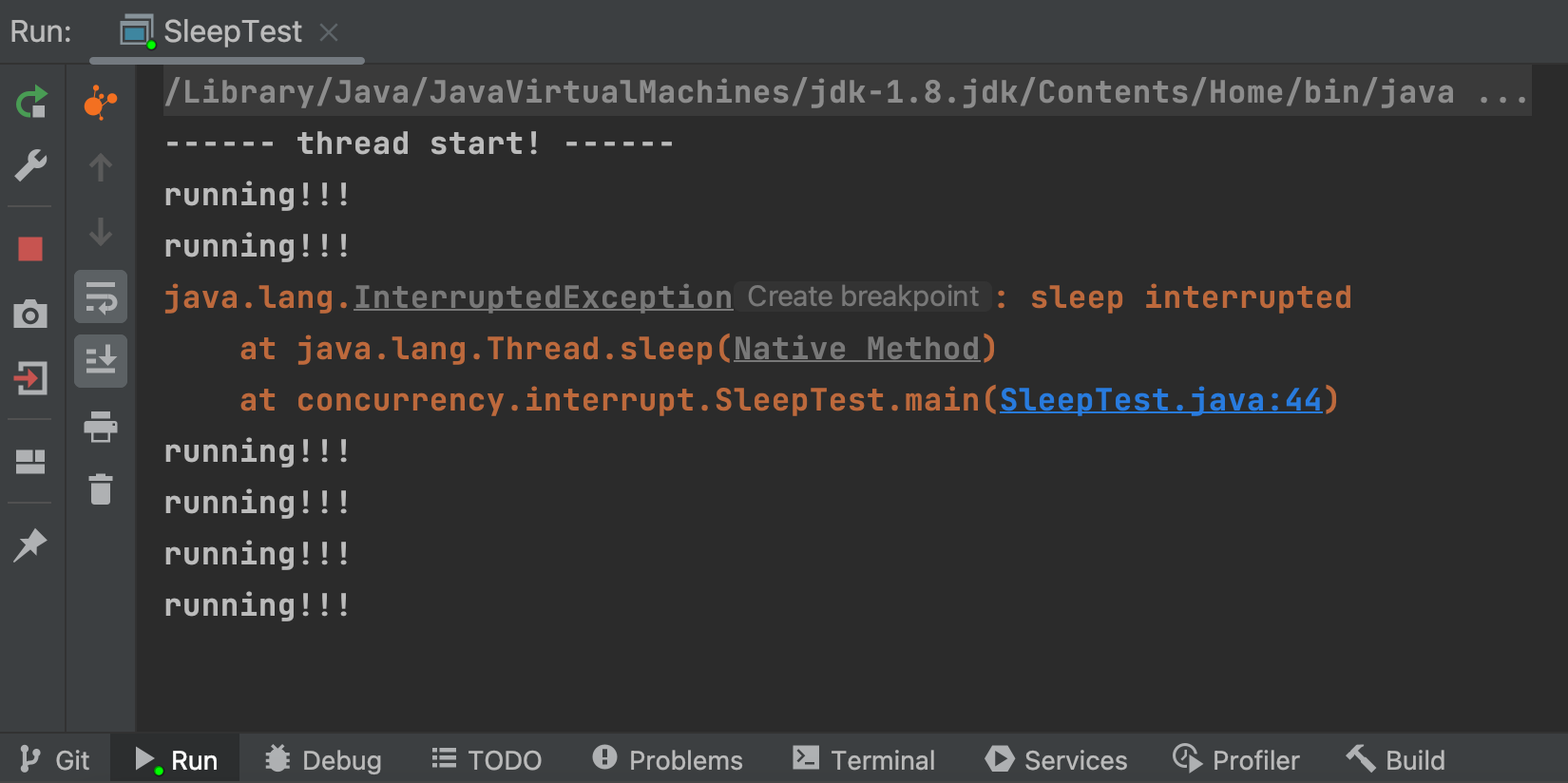
程序catch到受检异常InterruptedException后,执行 e.printStackTrace() 语句后吞掉了异常,导致出现while死循环。
FAQ
Q: 抛出 InterruptedException 异常后,中断标识就⼀定被清除(置为false)吗 ?
ans: 是的,线程中断标识一定会被清空。
Q: 处在死锁状态的线程是否可以被中断 ?
ans: 处于死锁状态的线程无法直接被中断。
Q: 已进⼊临界区的线程能否被中断 ?
ans: 已进入临界区的线程无法被直接中断。
程序示例
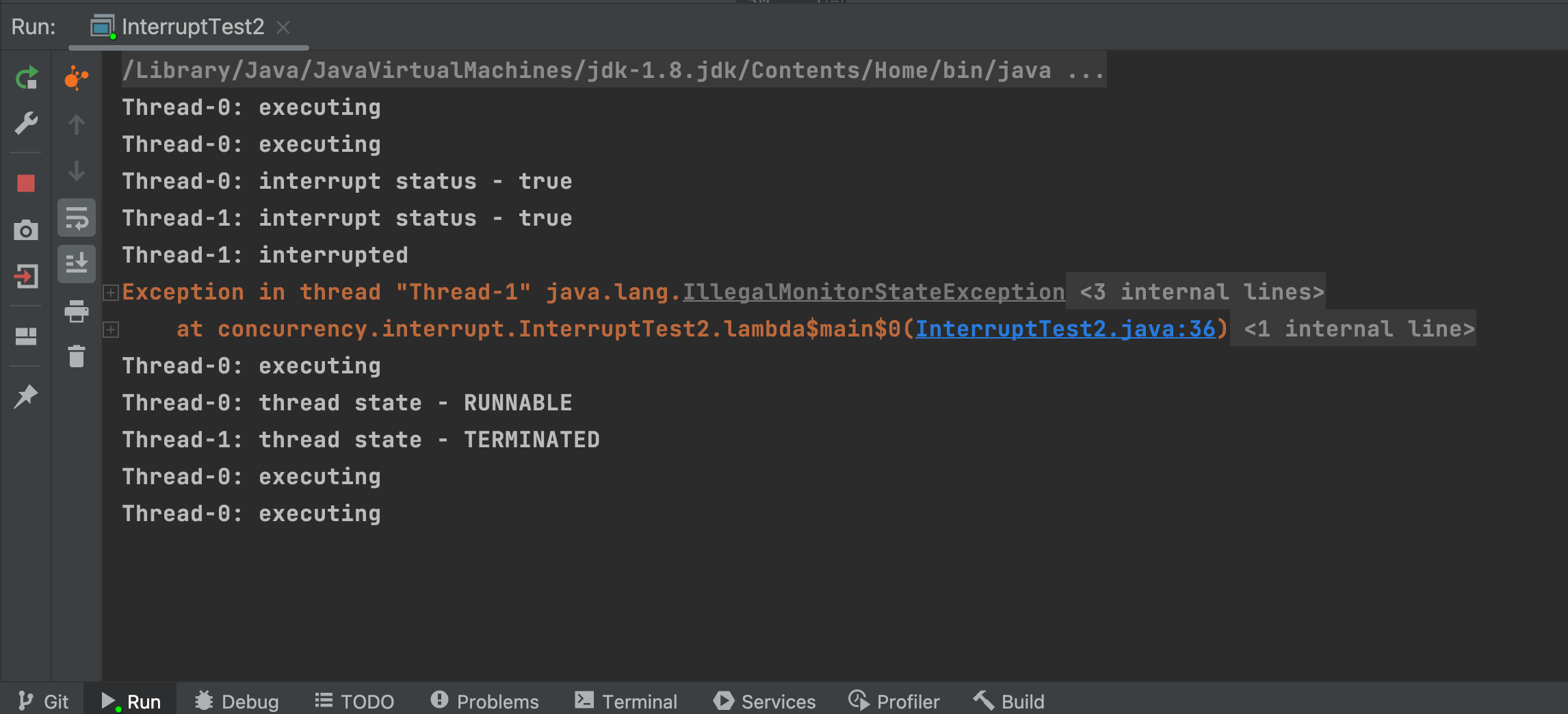
public class InterruptTest2 {
private static final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List<Thread> list = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 2;
for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 尝试获取锁,不可响应中断
lock.lock();
try {
// 执行临界区操作
while (true) {
// lock()方法虽然不可响应中断, 但可以使用isInterrupted()方法判断中断状态, 显示处理中断
// if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
// System.out.println("break!!!");
// break;
// }
System.out.println(name + ": executing");
for (int k = 0; k < Integer.MAX_VALUE; k++)
for (int l = 0; l < Integer.MAX_VALUE; l++);
}
} finally {
// 退出临界区,释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
});
thread.start();
list.add(thread);
}
Thread.sleep(2000L);
for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++) {
// 中断线程
list.get(i).interrupt();
System.out.println(list.get(i).getName() + ": interrupt status - " + list.get(i).isInterrupted());
}
Thread.sleep(1000L);
for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i).getName() + ": thread state - " + list.get(i).getState());
}
}
}
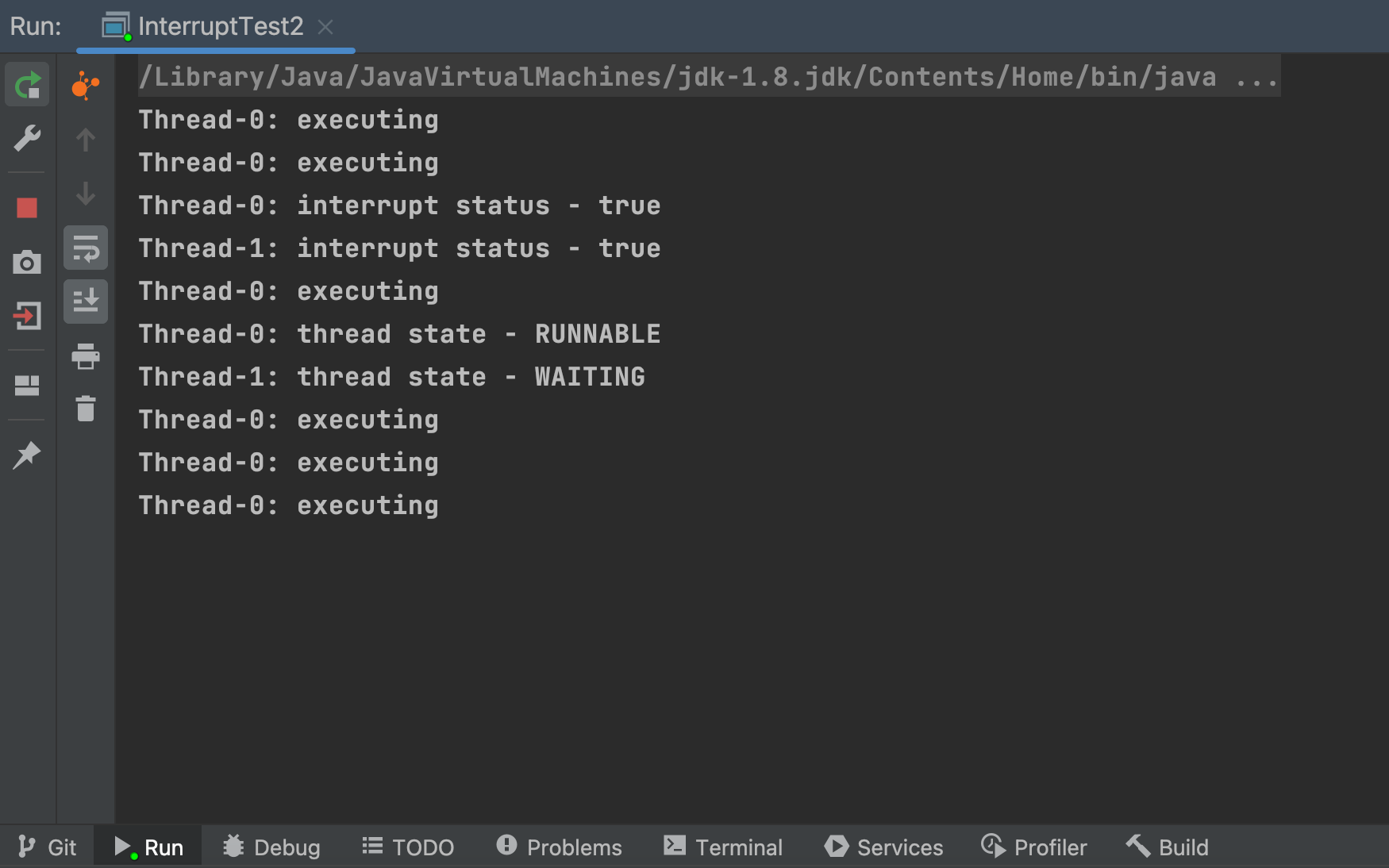
可以看到,已进入临界区的程序,无法响应中断,但可以在临界区程序中使用 isInterrupted() 等方法判断中断状态, 显示处理中断。
Q: 如果已进⼊临界区的线程不能被中断,有什么办法可以响应中断吗?
ans:
如果希望正在等待锁(acquiring)、等待 I/O 操作或处于睡眠状态的线程 响应中断,可以使用可重入锁(ReentrantLock)的 lock.lockInterruptibly() 方法;使用 lock.lockInterruptibly() 方法可以让正在阻塞等待获取锁(acquiring)的线程响应中断,抛出InterruptedException受检异常。
程序示例
public class InterruptTest2 {
private static final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List<Thread> list = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 2;
for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
try {
// 尝试获取锁,可响应中断
lock.lockInterruptibly();
// 执行临界区操作
while (true) {
System.out.println(name + ": executing");
for (int k = 0; k < Integer.MAX_VALUE; k++)
for (int m = 0; m < Integer.MAX_VALUE; m++);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(name + ": interrupted");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 退出临界区,释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
});
thread.start();
list.add(thread);
}
Thread.sleep(2000L);
for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++) {
// 中断线程
list.get(i).interrupt();
System.out.println(list.get(i).getName() + ": interrupt status - " + list.get(i).isInterrupted());
}
Thread.sleep(1000L);
for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i).getName() + ": thread state - " + list.get(i).getState());
}
}
}